HTML elements & Tree Structure
2. HTML elements & Tree Structure
2.1 HTML elements
An HTML element is defined by a start tag, some content, and an end tag. The HTML element is everything from the start tag to the end tag:
<tagname>Content goes here...</tagname>
Examples:
<h1>欢迎来到爬虫小组的网页!</h1>
<p>这是一个简单的测试页 </p>
| Start tag | Element content | End tag |
|---|---|---|
<h1> |
欢迎来到爬虫小组的网页 | </h1> |
<p> |
这是一个简单的测试页 | <p> |
<br> |
none | none |
Note: Some HTML elements have no content (like the <br> element). These elements are called empty elements. Empty elements do not have an end tag!
Common elements explained:
The
<!DOCTYPE html>declaration defines that this document is an HTML5 document.
The<html>element is the root element of an HTML page
The<head>element contains meta information about the HTML page
The<title>element specifies a title for the HTML page (which is shown in the browser’s title bar or in the page’s tab)
The<body>element defines the document’s body, and is a container for all the visible contents, such as headings, paragraphs, images, hyperlinks, tables, lists, etc.
The<h1><h2>element defines a large heading
The<p>element defines a paragraph
2.2 HTML Attributes
HTML attributes provide additional information about HTML elements. All HTML elements can have attributes. Attributes are always specified in the start tag. Attributes usually come in name/value pairs like: name=“value”.
-
The href Attribute:
The<a>tag defines a hyperlink. Thehrefattribute specifies the URL of the page the link goes to.
Example:
<a href="http://gitlabce.apps.dit-prdocp.novartis.net/YUHAY/web-crawler-do.git">Web Crawler DO</a> -
The src Attribute:
The<img>tag is used to embed an image in an HTML page. Thesrcattribute specifies the path to the image to be displayed.
Example:
<img src="https://www.w3schools.com/js/pic_bulboff.gif"> -
The style Attribute:
Thestyleattribute is used to add styles to an element, such as color, font, size, and more.
Example:
<img style="width:30px">
The
widthandheightattributes of<img>provide size information for images
Thealtattribute of<img>provides an alternate text for an image
Thelangattribute of the<html>tag declares the language of the Web page
Thetitleattribute defines some extra information about an element
2.3 Tree structure of HTML document
HTML documents can be treated as trees of nodes. Look at the following document:
<books>
<book>
<title lang="en">Harry Potter</title>
<author>J K. Rowling</author>
<year>2005</year>
<price>29.99</price>
</book>
</books>
The topmost element of the tree is called the root element. <books> is the root element node of the above tree. There are other element nodes, such as <author>J K. Rowling</author>, <year>2005</year>, etc.
It also looks like the path of computer file systems:
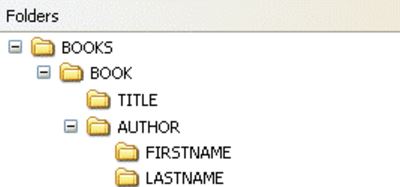
2.3.1 Relationship of Nodes
Example 1:
<book>
<title>Harry Potter</title>
<author>J K. Rowling</author>
<year>2005</year>
<price>29.99</price>
</book>
1. Parent
Each element has one parent.
In the example 1; the book element is the parent of the title, author, year, and price.
2. Children
Element nodes may have zero, one or more children.
In the example 1; the title, author, year, and price elements are all children of the book element.
3. Siblings
Nodes that have the same parent.
In the example 1; the title, author, year, and price elements are all siblings.
Example 2:
<books>
<book>
<title>Harry Potter</title>
<author>J K. Rowling</author>
<year>2005</year>
<price>29.99</price>
</book>
</books>
4. Ancestors
A node’s parent, parent’s parent, etc.
In the example 2; the ancestors of the title element are the book element and the books element.
5. Descendants
A node’s children, children’s children, etc.
In the example 2; descendants of the books element are the book, title, author, year, and price elements.